: 1. Penyiapan motherboard
Periksa buku manual motherboard untuk mengetahui posisi jumper untuk pengaturan CPU speed, speed multiplier dan tegangan masukan ke motherboard. Atur seting jumper sesuai petunjuk, kesalahan mengatur jumper tegangan dapat merusak prosessor.

2. Memasang Prosessor
- Tentukan posisi pin 1 pada prosessor dan socket prosessor di motherboard, umumnya terletak di pojok yang ditandai dengan titik, segitiga atau lekukan.
- Tegakkan posisi tuas pengunci socket untuk membuka.
- Masukkan prosessor ke socket dengan lebih dulu menyelaraskan posisi kaki-kaki prosessor dengan lubang socket. rapatkan hingga tidak terdapat celah antara prosessor dengan socket.
- Turunkan kembali tuas pengunci.
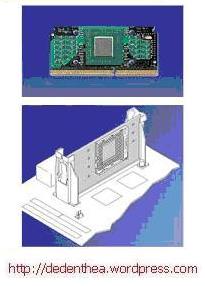
Jenis Slot

- Pasang penyangga (bracket) pada dua ujung slot di motherboard sehingga posisi lubang pasak bertemu dengan lubang di motherboard
- Masukkan pasak kemudian pengunci pasak pada lubang pasak
Selipkan card prosessor di antara kedua penahan dan tekan hingga tepat masuk ke lubang slot.
Beberapa jenis casing sudah dilengkapi power supply. Bila power supply belum disertakan maka cara pemasangannya sebagai berikut:
3. Memasang Heatsink
Fungsi heatsink adalah membuang panas yang dihasilkan oleh prosessor lewat konduksi panas dari prosessor ke heatsink.Untuk mengoptimalkan pemindahan panas maka heatsink harus dipasang rapat pada bagian atas prosessor dengan beberapa clip sebagai penahan sedangkan permukaan kontak pada heatsink dilapisi gen penghantar panas.Bila heatsink dilengkapi dengan fan maka konektor power pada fan dihubungkan ke konektor fan pada motherboard.

4. Memasang Modul Memori
Modul memori umumnya dipasang berurutan dari nomor socket terkecil. Urutan pemasangan dapat dilihat dari diagram motherboard.Setiap jenis modul memori yakni SIMM, DIMM dan RIMM dapat dibedakan dengan posisi lekukan pada sisi dan bawah pada modul.Cara memasang untuk tiap jenis modul memori sebagai berikut.
Jenis SIMM
- Sesuaikan posisi lekukan pada modul dengan tonjolan pada slot.
- Masukkan modul dengan membuat sudut miring 45 derajat terhadap slot
- Dorong hingga modul tegak pada slot, tuas pengunci pada slot akan otomatis mengunci modul.


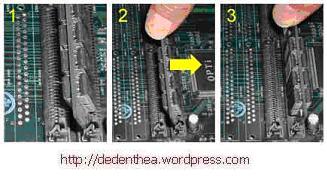
Jenis DIMM dan RIMM
Cara memasang modul DIMM dan RIMM sama dan hanya ada satu cara sehingga tidak akan terbalik karena ada dua lekukan sebagai panduan. Perbedaanya DIMM dan RIMM pada posisi lekukan
- Rebahkan kait pengunci pada ujung slot
- sesuaikan posisi lekukan pada konektor modul dengan tonjolan pada slot. lalu masukkan modul ke slot.
- Kait pengunci secara otomatis mengunci modul pada slot bila modul sudah tepat terpasang.

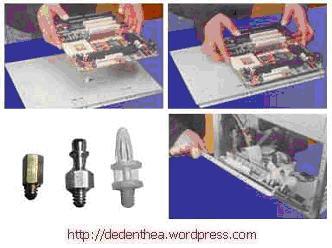
5. Memasang Motherboard pada Casing
Motherboard dipasang ke casing dengan sekerup dan dudukan (standoff). Cara pemasangannya sebagai berikut:
- Tentukan posisi lubang untuk setiap dudukan plastik dan logam. Lubang untuk dudukan logam (metal spacer) ditandai dengan cincin pada tepi lubang.
- Pasang dudukan logam atau plastik pada tray casing sesuai dengan posisi setiap lubang dudukan yang sesuai pada motherboard.
- Tempatkan motherboard pada tray casing sehinga kepala dudukan keluar dari lubang pada motherboard. Pasang sekerup pengunci pada setiap dudukan logam.
- Pasang bingkai port I/O (I/O sheild) pada motherboard jika ada.
- Pasang tray casing yang sudah terpasang motherboard pada casing dan kunci dengan sekerup.
6. Memasang Power Supply
- Masukkan power supply pada rak di bagian belakang casing. Pasang ke empat buah sekerup pengunci.
- HUbungkan konektor power dari power supply ke motherboard. Konektor power jenis ATX hanya memiliki satu cara pemasangan sehingga tidak akan terbalik. Untuk jenis non ATX dengan dua konektor yang terpisah maka kabel-kabel ground warna hitam harus ditempatkan bersisian dan dipasang pada bagian tengah dari konektor power motherboard. Hubungkan kabel daya untuk fan, jika memakai fan untuk pendingin CPU.

7. Memasang Kabel Motherboard dan Casing
Setelah motherboard terpasang di casing langkah selanjutnya adalah memasang kabel I/O pada motherboard dan panel dengan casing.
- Pasang kabel data untuk floppy drive pada konektor pengontrol floppy di motherboard
- Pasang kabel IDE untuk pada konektor IDE primary dan secondary pada motherboard.
- Untuk motherboard non ATX. Pasang kabel port serial dan pararel pada konektor di motherboard. Perhatikan posisi pin 1 untuk memasang.
- Pada bagian belakang casing terdapat lubang untuk memasang port tambahan jenis non slot. Buka sekerup pengunci pelat tertutup lubang port lalumasukkan port konektor yang ingin dipasang dan pasang sekerup kembali.
- Bila port mouse belum tersedia di belakang casing maka card konektor mouse harus dipasang lalu dihubungkan dengan konektor mouse pada motherboard.
- Hubungan kabel konektor dari switch di panel depan casing, LED, speaker internal dan port yang terpasang di depan casing bila ada ke motherboard. Periksa diagram motherboard untuk mencari lokasi konektor yang tepat.



8. Memasang Drive
Prosedur memasang drive hardisk, floppy, CD ROM, CD-RW atau DVD adalah sama sebagai berikut: Cara memasang adapter:Komputer yang baru selesai dirakit dapat diuji dengan menjalankan program setup BIOS. Cara melakukan pengujian dengan program BIOS sebagai berikut:
- Copot pelet penutup bay drive (ruang untuk drive pada casing)
- Masukkan drive dari depan bay dengan terlebih dahulu mengatur seting jumper (sebagai master atau slave) pada drive.
- Sesuaikan posisi lubang sekerup di drive dan casing lalu pasang sekerup penahan drive.
- Hubungkan konektor kabel IDE ke drive dan konektor di motherboard (konektor primary dipakai lebih dulu)
- Ulangi langkah 1 samapai 4 untuk setiap pemasangan drive.
- Bila kabel IDE terhubung ke du drive pastikan perbedaan seting jumper keduanya yakni drive pertama diset sebagai master dan lainnya sebagai slave.
- Konektor IDE secondary pada motherboard dapat dipakai untuk menghubungkan dua drive tambahan.
- Floppy drive dihubungkan ke konektor khusus floppy di motherboard
Sambungkan kabel power dari catu daya ke masing-masing drive.
Card adapter yang umum dipasang adalah video card, sound, network, modem dan SCSI adapter. Video card umumnya harus dipasang dan diinstall sebelum card adapter lainnya.

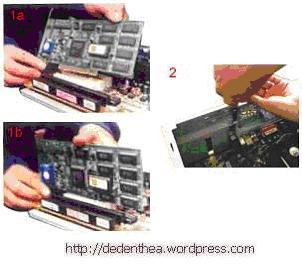
9. Memasang Card Adapter
- Pegang card adapter pada tepi, hindari menyentuh komponen atau rangkaian elektronik. Tekan card hingga konektor tepat masuk pada slot ekspansi di motherboard
- Pasang sekerup penahan card ke casing
- Hubungkan kembali kabel internal pada card, bila ada.
10. Penyelessaian Akhir
- Pasang penutup casing dengan menggeser
- sambungkan kabel dari catu daya ke soket dinding.
- Pasang konektor monitor ke port video card.
- Pasang konektor kabel telepon ke port modem bila ada.
- Hubungkan konektor kabel keyboard dan konektor mouse ke port mouse atau poert serial (tergantung jenis mouse).
- Hubungkan piranti eksternal lainnya seperti speaker, joystick, dan microphone bila ada ke port yang sesuai. Periksa manual dari card adapter untuk memastikan lokasi port.

2. Sebutkan jenis Port pada PC !
:Daftar Port Komputer :
Port Application Status
1/TCP,UDP TCP Port Service Multiplexer Official
2/TCP,UDP Management Utility Official
3/TCP,UDP Compression Process Official
5/TCP,UDP Remote Job Entry Official
7/TCP,UDP Echo Official
9/TCP,UDP Discard Official
11/TCP,UDP Active Users Official
13/TCP,UDP DAYTIME – (RFC 867) Official
17/TCP,UDP Quote of the Day Official
18/TCP,UDP Message Send Protocol Official
19/TCP,UDP Character Generator Official
20/TCP FTP – data Official
21/TCP FTP—control (command) Official
22/TCP,UDP Secure Shell (SSH)—used for secure logins, file transfers (scp, sftp) and port forwarding Official
23/TCP Telnet protocol—unencrypted text communications Official
25/TCP Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)—used for e-mail routing between mail servers Official
26/TCP,UDP RSFTP—a simple FTP-like protocol Unofficial
35/TCP,UDP Any private printer server protocol Official
35/TCP,UDP QMS Magicolor 2 printer server protocol Unofficial
37/TCP,UDP TIME protocol Official
39/TCP,UDP Resource Location Protocol[3] (RLP)—used for determining the location of higher level services from hosts on a network Official
41/TCP,UDP Graphics Official
42/TCP,UDP nameserver, ARPA Host Name Server Protocol Official
42/TCP,UDP WINS Unofficial
43/TCP WHOIS protocol Official
49/TCP,UDP TACACS Login Host protocol Official
52/TCP,UDP XNS (Xerox Network Services) Time Protocol Official
53/TCP,UDP Domain Name System (DNS) Official
54/TCP,UDP XNS (Xerox Network Services) Clearinghouse Official
56/TCP,UDP XNS (Xerox Network Services) Authentication Official
56/TCP,UDP RAP (Route Access Protocol)[4] Unofficial
57/TCP MTP, Mail Transfer Protocol Unofficial
58/TCP,UDP XNS (Xerox Network Services) Mail Official
67/UDP Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) Server; also used by Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Official
68/UDP Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) Client; also used by Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Official
69/UDP Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) Official
70/TCP Gopher protocol Official
79/TCP Finger protocol Official
80/TCP Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Official
81/TCP Torpark—Onion routing Unofficial
82/UDP Torpark—Control Unofficial
83/TCP MIT ML Device Official
88/TCP Kerberos—authentication system Official
90/TCP,UDP dnsix (DoD Network Security for Information Exchange) Securit Attribute Token Map Official
90/TCP,UDP Pointcast Unofficial
101/TCP NIC host name Official
102/TCP ISO-TSAP (Transport Service Access Point) Class 0 protocol[5] Official
104/TCP,UDP ACR/NEMA Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine Official
107/TCP Remote TELNET Service[6] protocol Official
109/TCP Post Office Protocol 2 (POP2) Official
110/TCP Post Office Protocol 3 (POP3) Official
111/TCP,UDP Sun Remote Procedure Call Official
113/TCP ident—old user identification system, still used by IRC servers to identify users Official
113/TCP,UDP Authentication Service (auth) Official
115/TCP Simple File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) Official
117/TCP UUCP Path Service Official
118/TCP,UDP SQL (Structured Query Language) Services Official
119/TCP Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP)—used for retrieving newsgroup messages Official
123/UDP Network Time Protocol (NTP)—used for time synchronization Official
135/TCP,UDP DCE endpoint resolution Official
135/TCP,UDP Microsoft EPMAP (End Point Mapper), also known as DCE/RPC Locator service[7], used to remotely manage services including DHCP server, DNS server and WINS Unofficial
137/TCP,UDP NetBIOS NetBIOS Name Service Official
138/TCP,UDP NetBIOS NetBIOS Datagram Service Official
139/TCP,UDP NetBIOS NetBIOS Session Service Official
143/TCP,UDP Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)—used for retrieving, organizing, and synchronizing e-mail messages Official
152/TCP,UDP Background File Transfer Program (BFTP)[8] Official
153/TCP,UDP SGMP, Simple Gateway Monitoring Protocol Official
156/TCP,UDP SQL Service Official
158/TCP,UDP DMSP, Distributed Mail Service Protocol Unofficial
161/TCP,UDP Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Official
162/TCP,UDP Simple Network Management Protocol Trap (SNMPTRAP)[9] Official
170/TCP Print-srv, Network PostScript Official
177/TCP,UDP X Display Manager Control Protocol (XDMCP) Official
179/TCP BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Official
194/TCP IRC (Internet Relay Chat) Official
201/TCP,UDP AppleTalk Routing Maintenance Official
209/TCP,UDP The Quick Mail Transfer Protocol Official
213/TCP,UDP IPX Official
218/TCP,UDP MPP, Message Posting Protocol Official
220/TCP,UDP IMAP, Interactive Mail Access Protocol, version 3 Official
259/TCP,UDP ESRO, Efficient Short Remote Operations Official
264/TCP,UDP BGMP, Border Gateway Multicast Protocol Official
311/TCP Mac OS X Server Admin (officially AppleShare IP Web admistration) Official
308/TCP Novastor Online Backup Official
318/TCP,UDP PKIX TSP, Time Stamp Protocol Official
323/TCP,UDP IMMP, Internet Message Mapping Protocol Unofficial
366/TCP,UDP ODMR, On-Demand Mail Relay Official
369/TCP,UDP Rpc2portmap Official
371/TCP,UDP ClearCase albd Official
383/TCP,UDP HP data alarm manager Official
384/TCP,UDP A Remote Network Server System Official
387/TCP,UDP AURP, AppleTalk Update-based Routing Protocol Official
389/TCP,UDP Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) Official
401/TCP,UDP UPS Uninterruptible Power Supply Official
402/TCP Altiris, Altiris Deployment Client Unofficial
411/TCP Direct Connect Hub Unofficial
412/TCP Direct Connect Client-to-Client Unofficial
427/TCP,UDP Service Location Protocol (SLP) Official
443/TCP Hypertext Transfer Protocol over TLS/SSL (HTTPS) Official
444/TCP,UDP SNPP, Simple Network Paging Protocol (RFC 1568) Official
445/TCP Microsoft-DS Active Directory, Windows shares Official
445/UDP Microsoft-DS SMB file sharing Official
464/TCP,UDP Kerberos Change/Set password Official
465/TCP Cisco protocol Unofficial
465/TCP SMTP over SSL Unofficial
475/TCP tcpnethaspsrv (Hasp services, TCP/IP version) Official
497/TCP Dantz Retrospect Official
500/UDP Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) Official
502/TCP,UDP Modbus, Protocol Unofficial
512/TCP Rexec, Remote Process Execution Official
512/UDP comsat, together with biff Official
513/TCP Login Official
513/UDP Who Official
514/TCP Shell—used to execute non-interactive commands on a remote system Official
514/UDP Syslog—used for system logging Official
515/TCP Line Printer Daemon—print service Official
517/UDP Talk Official
518/UDP NTalk Official
520/TCP efs, extended file name server Official
520/UDP Routing—RIP Official
524/TCP,UDP NCP (NetWare Core Protocol) is used for a variety things such as access to primary NetWare server resources, Time Synchronization, etc. Official
525/UDP Timed, Timeserver Official
530/TCP,UDP RPC Official
531/TCP,UDP AOL Instant Messenger, IRC Unofficial
532/TCP netnews Official
533/UDP netwall, For Emergency Broadcasts Official
540/TCP UUCP (Unix-to-Unix Copy Protocol) Official
542/TCP,UDP commerce (Commerce Applications) Official
543/TCP klogin, Kerberos login Official
544/TCP kshell, Kerberos Remote shell Official
546/TCP,UDP DHCPv6 client Official
547/TCP,UDP DHCPv6 server Official
548/TCP Apple Filing Protocol (AFP) over TCP Official
550/UDP new-rwho, new-who Official
554/TCP,UDP Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) Official
556/TCP Remotefs, RFS, rfs_server Official
560/UDP rmonitor, Remote Monitor Official
561/UDP monitor Official
563/TCP,UDP NNTP protocol over TLS/SSL (NNTPS) Official
587/TCP e-mail message submission[10] (SMTP) Official
591/TCP FileMaker 6.0 (and later) Web Sharing (HTTP Alternate, also see port 80) Official
593/TCP,UDP HTTP RPC Ep Map, Remote procedure call over Hypertext Transfer Protocol, often used by Distributed Component Object Model services and Microsoft Exchange Server Official
604/TCP TUNNEL profile[11], a protocol for BEEP peers to form an application layer tunnel Official
623/UDP ASF Remote Management and Control Protocol (ASF-RMCP) Official
631/TCP,UDP Internet Printing Protocol (IPP) Official
636/TCP,UDP Lightweight Directory Access Protocol over TLS/SSL (LDAPS) Official
639/TCP,UDP MSDP, Multicast Source Discovery Protocol Official
646/TCP,UDP LDP, Label Distribution Protocol, a routing protocol used in MPLS networks Official
647/TCP DHCP Failover protocol[12] Official
648/TCP RRP (Registry Registrar Protocol)[13] Official
652/TCP DTCP, Dynamic Tunnel Configuration Protocol Unofficial
654/TCP AODV (Ad-hoc On-demand Distance Vector) Official
655/TCP IEEE MMS (IEEE Media Management System)[14][15] Official
657/TCP,UDP IBM RMC (Remote monitoring and Control) protocol, used by System p5 AIX Integrated Virtualization Manager (IVM)[16] and Hardware Management Console to connect managed logical partitions (LPAR) to enable dynamic partition reconfiguration Official
660/TCP Mac OS X Server administration Official
665/TCP sun-dr, Remote Dynamic Reconfiguration Unofficial
666/UDP Doom, first online first-person shooter Official
674/TCP ACAP (Application Configuration Access Protocol) Official
691/TCP MS Exchange Routing Official
692/TCP Hyperwave-ISP Official
694/UDP Linux-HA High availability Heartbeat Unofficial
695/TCP IEEE-MMS-SSL (IEEE Media Management System over SSL)[17] Official
698/UDP OLSR (Optimized Link State Routing) Official
699/TCP Access Network Official
700/TCP EPP (Extensible Provisioning Protocol), a protocol for communication between domain name registries and registrars (RFC 4934) Official
701/TCP LMP (Link Management Protocol (Internet))[18], a protocol that runs between a pair of nodes and is used to manage traffic engineering (TE) links Official
702/TCP IRIS[19][20] (Internet Registry Information Service) over BEEP (Blocks Extensible Exchange Protocol)[21] (RFC 3983) Official
706/TCP SILC, Secure Internet Live Conferencing Official
711/TCP Cisco TDP, Tag Distribution Protocol[22][23][24]—being replaced by the MPLS Label Distribution Protocol[25] Official
712/TCP TBRPF, Topology Broadcast based on Reverse-Path Forwarding routing protocol (RFC 3684) Official
712/UDP Promise RAID Controller Unofficial
720/TCP SMQP, Simple Message Queue Protocol Unofficial
749/TCP,UDP Kerberos administration Official
750/TCP rfile Official
750/UDP loadav Official
750/UDP kerberos-iv, Kerberos version IV Official
751/TCP,UDP pump Official
751/TCP,UDP kerberos_master, Kerberos authentication Unofficial
752/TCP qrh Official
752/UDP qrh Official
752/UDP userreg_server, Kerberos Password (kpasswd) server Unofficial
753/TCP Reverse Routing Header (rrh)[26] Official
753/UDP Reverse Routing Header (rrh) Official
753/UDP passwd_server, Kerberos userreg server Unofficial
754/TCP tell send Official
754/TCP krb5_prop, Kerberos v5 slave propagation Unofficial
754/UDP tell send Official
760/TCP,UDP ns Official
760/TCP,UDP krbupdate [kreg], Kerberos registration Unofficial
782/TCP Conserver serial-console management server Unofficial
783/TCP SpamAssassin spamd daemon Unofficial
829/TCP CMP (Certificate Management Protocol) Unofficial
860/TCP iSCSI (RFC 3720) Official
873/TCP rsync file synchronisation protocol Official
888/TCP cddbp, CD DataBase (CDDB) protocol (CDDBP)—unassigned but widespread use Unofficial
901/TCP Samba Web Administration Tool (SWAT) Unofficial
901/TCP, UDP VMware Virtual Infrastructure Client (UDP from server being managed to management console) Unofficial
902/TCP VMware Server Console (TCP from management console to server being Managed)[27] Unofficial
904/TCP VMware Server Alternate (if 902 is in use, i.e. SUSE linux) Unofficial
911/TCP Network Console on Acid (NCA)—local tty redirection over OpenSSH Unofficial
953/TCP,UDP Domain Name System (DNS) RDNC Service Official
981/TCP SofaWare Technologies Remote HTTPS management for firewall devices running embedded Check Point FireWall-1 software Unofficial
989/TCP,UDP FTPS Protocol (data): FTP over TLS/SSL Official
990/TCP,UDP FTPS Protocol (control): FTP over TLS/SSL Official
991/TCP,UDP NAS (Netnews Administration System) Official
992/TCP,UDP TELNET protocol over TLS/SSL Official
993/TCP Internet Message Access Protocol over SSL (IMAPS) Official
995/TCP Post Office Protocol 3 over TLS/SSL (POP3S) Official
1023/TCP,UDP Reserved[1]
1/TCP,UDP TCP Port Service Multiplexer Official
2/TCP,UDP Management Utility Official
3/TCP,UDP Compression Process Official
5/TCP,UDP Remote Job Entry Official
7/TCP,UDP Echo Official
9/TCP,UDP Discard Official
11/TCP,UDP Active Users Official
13/TCP,UDP DAYTIME – (RFC 867) Official
17/TCP,UDP Quote of the Day Official
18/TCP,UDP Message Send Protocol Official
19/TCP,UDP Character Generator Official
20/TCP FTP – data Official
21/TCP FTP—control (command) Official
22/TCP,UDP Secure Shell (SSH)—used for secure logins, file transfers (scp, sftp) and port forwarding Official
23/TCP Telnet protocol—unencrypted text communications Official
25/TCP Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)—used for e-mail routing between mail servers Official
26/TCP,UDP RSFTP—a simple FTP-like protocol Unofficial
35/TCP,UDP Any private printer server protocol Official
35/TCP,UDP QMS Magicolor 2 printer server protocol Unofficial
37/TCP,UDP TIME protocol Official
39/TCP,UDP Resource Location Protocol[3] (RLP)—used for determining the location of higher level services from hosts on a network Official
41/TCP,UDP Graphics Official
42/TCP,UDP nameserver, ARPA Host Name Server Protocol Official
42/TCP,UDP WINS Unofficial
43/TCP WHOIS protocol Official
49/TCP,UDP TACACS Login Host protocol Official
52/TCP,UDP XNS (Xerox Network Services) Time Protocol Official
53/TCP,UDP Domain Name System (DNS) Official
54/TCP,UDP XNS (Xerox Network Services) Clearinghouse Official
56/TCP,UDP XNS (Xerox Network Services) Authentication Official
56/TCP,UDP RAP (Route Access Protocol)[4] Unofficial
57/TCP MTP, Mail Transfer Protocol Unofficial
58/TCP,UDP XNS (Xerox Network Services) Mail Official
67/UDP Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) Server; also used by Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Official
68/UDP Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) Client; also used by Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Official
69/UDP Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) Official
70/TCP Gopher protocol Official
79/TCP Finger protocol Official
80/TCP Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) Official
81/TCP Torpark—Onion routing Unofficial
82/UDP Torpark—Control Unofficial
83/TCP MIT ML Device Official
88/TCP Kerberos—authentication system Official
90/TCP,UDP dnsix (DoD Network Security for Information Exchange) Securit Attribute Token Map Official
90/TCP,UDP Pointcast Unofficial
101/TCP NIC host name Official
102/TCP ISO-TSAP (Transport Service Access Point) Class 0 protocol[5] Official
104/TCP,UDP ACR/NEMA Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine Official
107/TCP Remote TELNET Service[6] protocol Official
109/TCP Post Office Protocol 2 (POP2) Official
110/TCP Post Office Protocol 3 (POP3) Official
111/TCP,UDP Sun Remote Procedure Call Official
113/TCP ident—old user identification system, still used by IRC servers to identify users Official
113/TCP,UDP Authentication Service (auth) Official
115/TCP Simple File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) Official
117/TCP UUCP Path Service Official
118/TCP,UDP SQL (Structured Query Language) Services Official
119/TCP Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP)—used for retrieving newsgroup messages Official
123/UDP Network Time Protocol (NTP)—used for time synchronization Official
135/TCP,UDP DCE endpoint resolution Official
135/TCP,UDP Microsoft EPMAP (End Point Mapper), also known as DCE/RPC Locator service[7], used to remotely manage services including DHCP server, DNS server and WINS Unofficial
137/TCP,UDP NetBIOS NetBIOS Name Service Official
138/TCP,UDP NetBIOS NetBIOS Datagram Service Official
139/TCP,UDP NetBIOS NetBIOS Session Service Official
143/TCP,UDP Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)—used for retrieving, organizing, and synchronizing e-mail messages Official
152/TCP,UDP Background File Transfer Program (BFTP)[8] Official
153/TCP,UDP SGMP, Simple Gateway Monitoring Protocol Official
156/TCP,UDP SQL Service Official
158/TCP,UDP DMSP, Distributed Mail Service Protocol Unofficial
161/TCP,UDP Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Official
162/TCP,UDP Simple Network Management Protocol Trap (SNMPTRAP)[9] Official
170/TCP Print-srv, Network PostScript Official
177/TCP,UDP X Display Manager Control Protocol (XDMCP) Official
179/TCP BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) Official
194/TCP IRC (Internet Relay Chat) Official
201/TCP,UDP AppleTalk Routing Maintenance Official
209/TCP,UDP The Quick Mail Transfer Protocol Official
213/TCP,UDP IPX Official
218/TCP,UDP MPP, Message Posting Protocol Official
220/TCP,UDP IMAP, Interactive Mail Access Protocol, version 3 Official
259/TCP,UDP ESRO, Efficient Short Remote Operations Official
264/TCP,UDP BGMP, Border Gateway Multicast Protocol Official
311/TCP Mac OS X Server Admin (officially AppleShare IP Web admistration) Official
308/TCP Novastor Online Backup Official
318/TCP,UDP PKIX TSP, Time Stamp Protocol Official
323/TCP,UDP IMMP, Internet Message Mapping Protocol Unofficial
366/TCP,UDP ODMR, On-Demand Mail Relay Official
369/TCP,UDP Rpc2portmap Official
371/TCP,UDP ClearCase albd Official
383/TCP,UDP HP data alarm manager Official
384/TCP,UDP A Remote Network Server System Official
387/TCP,UDP AURP, AppleTalk Update-based Routing Protocol Official
389/TCP,UDP Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) Official
401/TCP,UDP UPS Uninterruptible Power Supply Official
402/TCP Altiris, Altiris Deployment Client Unofficial
411/TCP Direct Connect Hub Unofficial
412/TCP Direct Connect Client-to-Client Unofficial
427/TCP,UDP Service Location Protocol (SLP) Official
443/TCP Hypertext Transfer Protocol over TLS/SSL (HTTPS) Official
444/TCP,UDP SNPP, Simple Network Paging Protocol (RFC 1568) Official
445/TCP Microsoft-DS Active Directory, Windows shares Official
445/UDP Microsoft-DS SMB file sharing Official
464/TCP,UDP Kerberos Change/Set password Official
465/TCP Cisco protocol Unofficial
465/TCP SMTP over SSL Unofficial
475/TCP tcpnethaspsrv (Hasp services, TCP/IP version) Official
497/TCP Dantz Retrospect Official
500/UDP Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP) Official
502/TCP,UDP Modbus, Protocol Unofficial
512/TCP Rexec, Remote Process Execution Official
512/UDP comsat, together with biff Official
513/TCP Login Official
513/UDP Who Official
514/TCP Shell—used to execute non-interactive commands on a remote system Official
514/UDP Syslog—used for system logging Official
515/TCP Line Printer Daemon—print service Official
517/UDP Talk Official
518/UDP NTalk Official
520/TCP efs, extended file name server Official
520/UDP Routing—RIP Official
524/TCP,UDP NCP (NetWare Core Protocol) is used for a variety things such as access to primary NetWare server resources, Time Synchronization, etc. Official
525/UDP Timed, Timeserver Official
530/TCP,UDP RPC Official
531/TCP,UDP AOL Instant Messenger, IRC Unofficial
532/TCP netnews Official
533/UDP netwall, For Emergency Broadcasts Official
540/TCP UUCP (Unix-to-Unix Copy Protocol) Official
542/TCP,UDP commerce (Commerce Applications) Official
543/TCP klogin, Kerberos login Official
544/TCP kshell, Kerberos Remote shell Official
546/TCP,UDP DHCPv6 client Official
547/TCP,UDP DHCPv6 server Official
548/TCP Apple Filing Protocol (AFP) over TCP Official
550/UDP new-rwho, new-who Official
554/TCP,UDP Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) Official
556/TCP Remotefs, RFS, rfs_server Official
560/UDP rmonitor, Remote Monitor Official
561/UDP monitor Official
563/TCP,UDP NNTP protocol over TLS/SSL (NNTPS) Official
587/TCP e-mail message submission[10] (SMTP) Official
591/TCP FileMaker 6.0 (and later) Web Sharing (HTTP Alternate, also see port 80) Official
593/TCP,UDP HTTP RPC Ep Map, Remote procedure call over Hypertext Transfer Protocol, often used by Distributed Component Object Model services and Microsoft Exchange Server Official
604/TCP TUNNEL profile[11], a protocol for BEEP peers to form an application layer tunnel Official
623/UDP ASF Remote Management and Control Protocol (ASF-RMCP) Official
631/TCP,UDP Internet Printing Protocol (IPP) Official
636/TCP,UDP Lightweight Directory Access Protocol over TLS/SSL (LDAPS) Official
639/TCP,UDP MSDP, Multicast Source Discovery Protocol Official
646/TCP,UDP LDP, Label Distribution Protocol, a routing protocol used in MPLS networks Official
647/TCP DHCP Failover protocol[12] Official
648/TCP RRP (Registry Registrar Protocol)[13] Official
652/TCP DTCP, Dynamic Tunnel Configuration Protocol Unofficial
654/TCP AODV (Ad-hoc On-demand Distance Vector) Official
655/TCP IEEE MMS (IEEE Media Management System)[14][15] Official
657/TCP,UDP IBM RMC (Remote monitoring and Control) protocol, used by System p5 AIX Integrated Virtualization Manager (IVM)[16] and Hardware Management Console to connect managed logical partitions (LPAR) to enable dynamic partition reconfiguration Official
660/TCP Mac OS X Server administration Official
665/TCP sun-dr, Remote Dynamic Reconfiguration Unofficial
666/UDP Doom, first online first-person shooter Official
674/TCP ACAP (Application Configuration Access Protocol) Official
691/TCP MS Exchange Routing Official
692/TCP Hyperwave-ISP Official
694/UDP Linux-HA High availability Heartbeat Unofficial
695/TCP IEEE-MMS-SSL (IEEE Media Management System over SSL)[17] Official
698/UDP OLSR (Optimized Link State Routing) Official
699/TCP Access Network Official
700/TCP EPP (Extensible Provisioning Protocol), a protocol for communication between domain name registries and registrars (RFC 4934) Official
701/TCP LMP (Link Management Protocol (Internet))[18], a protocol that runs between a pair of nodes and is used to manage traffic engineering (TE) links Official
702/TCP IRIS[19][20] (Internet Registry Information Service) over BEEP (Blocks Extensible Exchange Protocol)[21] (RFC 3983) Official
706/TCP SILC, Secure Internet Live Conferencing Official
711/TCP Cisco TDP, Tag Distribution Protocol[22][23][24]—being replaced by the MPLS Label Distribution Protocol[25] Official
712/TCP TBRPF, Topology Broadcast based on Reverse-Path Forwarding routing protocol (RFC 3684) Official
712/UDP Promise RAID Controller Unofficial
720/TCP SMQP, Simple Message Queue Protocol Unofficial
749/TCP,UDP Kerberos administration Official
750/TCP rfile Official
750/UDP loadav Official
750/UDP kerberos-iv, Kerberos version IV Official
751/TCP,UDP pump Official
751/TCP,UDP kerberos_master, Kerberos authentication Unofficial
752/TCP qrh Official
752/UDP qrh Official
752/UDP userreg_server, Kerberos Password (kpasswd) server Unofficial
753/TCP Reverse Routing Header (rrh)[26] Official
753/UDP Reverse Routing Header (rrh) Official
753/UDP passwd_server, Kerberos userreg server Unofficial
754/TCP tell send Official
754/TCP krb5_prop, Kerberos v5 slave propagation Unofficial
754/UDP tell send Official
760/TCP,UDP ns Official
760/TCP,UDP krbupdate [kreg], Kerberos registration Unofficial
782/TCP Conserver serial-console management server Unofficial
783/TCP SpamAssassin spamd daemon Unofficial
829/TCP CMP (Certificate Management Protocol) Unofficial
860/TCP iSCSI (RFC 3720) Official
873/TCP rsync file synchronisation protocol Official
888/TCP cddbp, CD DataBase (CDDB) protocol (CDDBP)—unassigned but widespread use Unofficial
901/TCP Samba Web Administration Tool (SWAT) Unofficial
901/TCP, UDP VMware Virtual Infrastructure Client (UDP from server being managed to management console) Unofficial
902/TCP VMware Server Console (TCP from management console to server being Managed)[27] Unofficial
904/TCP VMware Server Alternate (if 902 is in use, i.e. SUSE linux) Unofficial
911/TCP Network Console on Acid (NCA)—local tty redirection over OpenSSH Unofficial
953/TCP,UDP Domain Name System (DNS) RDNC Service Official
981/TCP SofaWare Technologies Remote HTTPS management for firewall devices running embedded Check Point FireWall-1 software Unofficial
989/TCP,UDP FTPS Protocol (data): FTP over TLS/SSL Official
990/TCP,UDP FTPS Protocol (control): FTP over TLS/SSL Official
991/TCP,UDP NAS (Netnews Administration System) Official
992/TCP,UDP TELNET protocol over TLS/SSL Official
993/TCP Internet Message Access Protocol over SSL (IMAPS) Official
995/TCP Post Office Protocol 3 over TLS/SSL (POP3S) Official
1023/TCP,UDP Reserved[1]
3 . Sebutkan jenis-jenis slot pada PC !
: * Slot AGP
* Slot PCI
* Slot PCI Express 16
4 . Buatlah Sebuah Spesifikasi ( Dekstop Pc ) !
: Platform Netbook
Processor Type Intel Atom Processor
Processor Onboard Intel Atom Dual Core N570 Processor (1.66 GHz, Cache 1 MB)
Chipset Intel NM10
Standard Memory 1 GB DDR3 SODIMM PC-10600
Max. Memory 1 GB (1 DIMM)
Video Type Intel® Graphics Media Accelerator 3150 256 MB (shared)
Display Size 10.1" WSVGA LED
Display Max. Resolution 1024 x 600
Display Technology LED Anti Glare
Audio Type Integrated
Speakers Type Integrated
Floppy Drive Optional
Hard Drive Type 320 GB Serial ATA 7200 RPM
Networking Integrated
Network Speed 10 / 100 Mbps
Wireless Network Type Integrated
Wireless Network Protocol IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g, IEEE 802.11n
Wireless Bluetooth Available
Keyboard Type Full size
Input Device Type Touch Pad
Card Reader Provided SD, MMC
Interface Provided 3x USB 2.0, VGA, LAN, Audio
O/S Provided Pre-sales Request Available
Battery Type Rechargeable Lithium-ion Battery
Power Supply External AC Adapter
Weight 1.14 Kg
Standard Warranty 1-year Limited Warranty by Authorized Distributor
Bundled Peripherals Optional
Package Contents Contents may vary
Processor Onboard Intel Atom Dual Core N570 Processor (1.66 GHz, Cache 1 MB)
Chipset Intel NM10
Standard Memory 1 GB DDR3 SODIMM PC-10600
Max. Memory 1 GB (1 DIMM)
Video Type Intel® Graphics Media Accelerator 3150 256 MB (shared)
Display Size 10.1" WSVGA LED
Display Max. Resolution 1024 x 600
Display Technology LED Anti Glare
Audio Type Integrated
Speakers Type Integrated
Floppy Drive Optional
Hard Drive Type 320 GB Serial ATA 7200 RPM
Networking Integrated
Network Speed 10 / 100 Mbps
Wireless Network Type Integrated
Wireless Network Protocol IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g, IEEE 802.11n
Wireless Bluetooth Available
Keyboard Type Full size
Input Device Type Touch Pad
Card Reader Provided SD, MMC
Interface Provided 3x USB 2.0, VGA, LAN, Audio
O/S Provided Pre-sales Request Available
Battery Type Rechargeable Lithium-ion Battery
Power Supply External AC Adapter
Weight 1.14 Kg
Standard Warranty 1-year Limited Warranty by Authorized Distributor
Bundled Peripherals Optional
Package Contents Contents may vary
5 . Jelaskan perbedaan prosessor intel Core i3,i5,i7 !
:
core i3
Core i3 ini dimaksudkan untuk menjadi low end baru dari garis kinerja prosesordari Intel, setelah pensiun dari merek Core 2. [18] [19]
Prosesor Core pertama i3 diluncurkan pada tanggal 7 Januari 2010. [20]
I3 Nehalem Core pertama berbasis adalah Clarkdale berbasis, dengan GPU terintegrasi dan dua core. [21] Prosesor yang sama juga tersedia sebagai Corei5 dan Pentium, dengan konfigurasi sedikit berbeda.
Core i3-3xxM prosesor didasarkan pada Arrandale, versi mobile dari prosesor desktop Clarkdale. Mereka adalah mirip dengan seri i5-4xx Inti tetapi berjalanpada kecepatan clock yang lebih rendah dan tanpa Turbo Boost [22]. Menurut sebuah FAQ Intel mereka tidak mendukung Kode Koreksi Kesalahan (ECC)memori [23]. Menurut memproduksi motherboard Supermicro jika prosesor Core i3 digunakan dengan platform chipset server seperti Intel 3400/3420/3450, CPU akan mendukung ECC dengan UDIMM [24]. Ketika ditanya, Intel menegaskan bahwa, meskipun Intel chipset seri 5 mendukung memori non-ECC hanya denganprosesor Core i5 atau i3, menggunakan mereka prosesor pada motherboard dengan chipset seri 3400 akan mendukung fungsi ECC memori ECC
core i5
Core i5 pertama [26] menggunakan mikroarsitektur Nehalem diperkenalkan pada tanggal 8 September 2009 sebagai varian utama dari Core i7 sebelumnya, [27]inti Lynnfield. Lynnfield Core i5 memiliki 8 MB L3 cache, bus DMI berjalan pada2,5 GT / s dan dukungan untuk dual-channel memori DDR3-800/1066/1333 dan memiliki Hyper-threading dinonaktifkan. Prosesor yang sama dengan set fituryang berbeda (frekuensi clock Hyper-Threading dan lainnya) yang aktif dijual sebagai Core i7-8xx dan Xeon 3400-series prosesor, yang tidak harus bingungdengan high-end Core i7-9xx dan Xeon 3500-series prosesor berdasarkanBloomfield.Core i5-5xx prosesor mobile yang bernama Arrandale dan berdasarkan pada 32nm Westmere mengecilkan dari mikroarsitektur Nehalem. Prosesor Arrandaletelah terintegrasi kemampuan grafis tetapi hanya dua core prosesor. Mereka dibebaskan pada Januari 2010, bersama dengan prosesor i7-6xx dan Corei3-3xx Inti berbasis pada chip yang sama. Cache L3 di Core i5-5xx prosesorberkurang menjadi 3 MB, sedangkan Core i5-6xx akan menggunakan cachepenuh dan Core i3-3xx tidak akan memiliki dukungan untuk Turbo Boost [28].Clarkdale, versi desktop Arrandale , yang dijual sebagai core i5-6xx, bersama dengan core i3 terkait dan merek Pentium. Ini memiliki Hyper-Threadingdiaktifkan dan 4 purna MB L3 cache. [29]
Menurut Intel "prosesor desktop Core i5 dan papan desktop yang biasanya tidak mendukung memori ECC."
Core i7Intel Core i7 adalah merek Intel nama untuk beberapa keluarga desktop dan laptop 64-bit x86-64 prosesor dengan menggunakan Nehalem, Westmere, dan microarchitectures Sandy Bridge. Merek Core i7 ditargetkan pada bisnis dan high-end pasar konsumen untuk kedua komputer desktop dan laptop, [32] dan dibedakan dari Core i3 (entry level konsumen), Core i5 (konsumen mainstream) dan Xeon (server dan workstation) merek.Nama Core i7 diperkenalkan dengan prosesor Quad-core Bloomfield pada akhir 2008. [33] [34] [35] [36] Pada tahun 2009 model Core i7 baru berdasarkan Lynnfield prosesor desktop quad-core dan quad-core Clarksfield ponsel yang ditambahkan [37], dan model didasarkan pada prosesor dual-core Arrandale ponsel ditambahkan pada Januari 2010. Prosesor enam-core pertama di jajaran Core adalah Gulftown, yang diluncurkan pada 16 Maret 2010. Baik Core i7 reguler dan Extreme Edition diiklankan sebagai bintang lima di Processor Intel Rating. Pada bulan Januari 2011, Intel merilis generasi kedua dari prosesor i7 inti. Kedua generasi pertama dan kedua dari prosesor Intel i7 inti dinilai sebagai bintang 5 di peringkat prosesor Intel. Generasi 2 dari prosesor Intel inti didasarkan pada inti 'Sandy Bridge' dan diatur untuk diperbarui pada Januari 2012 dengan 'Ivy Bridge'Dalam setiap dari tiga generasi pertama mikroarsitektur dari merek, Core i7 memiliki anggota keluarga yang menggunakan dua tingkat sistem yang berbeda arsitektur, dan karena itu dua soket yang berbeda. [Kutipan diperlukan] Pada setiap generasi, prosesor Core i7 berkinerja tertinggi menggunakan soket yang sama dan QPI berbasis arsitektur sebagai low-end prosesor Xeon generasi itu, sementara prosesor Core i7 berkinerja rendah menggunakan soket yang sama dan PCIe / DMI / FDI arsitektur sebagai Core i5."Core i7" adalah penerus untuk merek Intel Core 2 [38] [39]. [40] [41] menyatakan bahwa perwakilan Intel Core i7 moniker dimaksudkan untuk membantu konsumen memutuskan untuk membeli prosesor baru sebagai berbasis Nehalem produk yang dirilis di masa depan.
Core i7Intel Core i7 adalah merek Intel nama untuk beberapa keluarga desktop dan laptop 64-bit x86-64 prosesor dengan menggunakan Nehalem, Westmere, dan microarchitectures Sandy Bridge. Merek Core i7 ditargetkan pada bisnis dan high-end pasar konsumen untuk kedua komputer desktop dan laptop, [32] dan dibedakan dari Core i3 (entry level konsumen), Core i5 (konsumen mainstream) dan Xeon (server dan workstation) merek.Nama Core i7 diperkenalkan dengan prosesor Quad-core Bloomfield pada akhir 2008. [33] [34] [35] [36] Pada tahun 2009 model Core i7 baru berdasarkan Lynnfield prosesor desktop quad-core dan quad-core Clarksfield ponsel yang ditambahkan [37], dan model didasarkan pada prosesor dual-core Arrandale ponsel ditambahkan pada Januari 2010. Prosesor enam-core pertama di jajaran Core adalah Gulftown, yang diluncurkan pada 16 Maret 2010. Baik Core i7 reguler dan Extreme Edition diiklankan sebagai bintang lima di Processor Intel Rating. Pada bulan Januari 2011, Intel merilis generasi kedua dari prosesor i7 inti. Kedua generasi pertama dan kedua dari prosesor Intel i7 inti dinilai sebagai bintang 5 di peringkat prosesor Intel. Generasi 2 dari prosesor Intel inti didasarkan pada inti 'Sandy Bridge' dan diatur untuk diperbarui pada Januari 2012 dengan 'Ivy Bridge'Dalam setiap dari tiga generasi pertama mikroarsitektur dari merek, Core i7 memiliki anggota keluarga yang menggunakan dua tingkat sistem yang berbeda arsitektur, dan karena itu dua soket yang berbeda. [Kutipan diperlukan] Pada setiap generasi, prosesor Core i7 berkinerja tertinggi menggunakan soket yang sama dan QPI berbasis arsitektur sebagai low-end prosesor Xeon generasi itu, sementara prosesor Core i7 berkinerja rendah menggunakan soket yang sama dan PCIe / DMI / FDI arsitektur sebagai Core i5."Core i7" adalah penerus untuk merek Intel Core 2 [38] [39]. [40] [41] menyatakan bahwa perwakilan Intel Core i7 moniker dimaksudkan untuk membantu konsumen memutuskan untuk membeli prosesor baru sebagai berbasis Nehalem produk yang dirilis di masa depan.